临界区、线程锁和互斥体
临界区、线程锁和互斥体
不可重入函数
不可重入函数: 当这个函数返回前,不可以被其他线程调用
原因:
printf : 访问了引用全局变量stdout
malloc : 引用了全局内存分配表
free : 引用的全局内存分配表
类似的 假如我在我的线程中使用全局变量会不会出现类似问题?
不可重入函数: 当这个函数返回前,不可以被其他线程调用
原因:
printf : 访问了引用全局变量stdout
malloc : 引用了全局内存分配表
free : 引用的全局内存分配表
类似的 假如我在我的线程中使用全局变量会不会出现类似问题?
HY0XH-D508H-081U8-JA2GH-CCUM2
4C4WK-8KH8L-H85J0-UHCNK-8CKQ8
NV09R-2W007-08D38-CA956-33U28
JU400-6EK4L-080V9-QT8EP-2KAQ2
NC6HH-26J4N-48098-Y0AX0-1GA66
HY0J0-6L28H-081W8-4TCN0-32RP0
0V012-002DJ-480T1-UHAE0-9GULF
4G6WR-A0K4M-08420-J8CN6-8A2QA
MF00U-65K53-H8DF9-Q20ZH-26R40
JV6D2-6YLDN-088C0-Q92N2-8Z00A
HG49R-2234J-08EJ8-WC9E2-87H2D
NV6TR-D4HD1-M84L1-P19QM-0PK3D
JG2JK-DM01L-M8101-J8AZH-3LUH2
进程和线程的关系:进程提供资源,线程使用资源完成工作
HANDLE CreateThread(
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, // SD /安全属性
DWORD dwStackSize, // initial stack size //线程栈大小-
LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE lpStartAddress, // thread function //线程代码
LPVOID lpParameter, // thread argument //线程参数
DWORD dwCreationFlags, // creation option //创建标识
LPDWORD lpThreadId // thread identifier //线程id
);
//线程等待
//等待一个
DWORD WaitForSingleObject(
HANDLE hHandle, // handle to object,监视对象的句柄
DWORD dwMilliseconds // time-out interval 指定超时等待时间 毫秒为单位
);
//等待多个
DWORD WaitForMultipleObjects(
DWORD nCount, // number of handles in array,句柄数量
CONST HANDLE *lpHandles, // object-handle array 句柄数组
BOOL fWaitAll, // wait option 是否全等待/TRUE 全部结束才返回/False 一个结束就返回
DWORD dwMilliseconds // time-out interval,超时时间
);
//获取线程的退出代码
BOOL GetExitCodeThread(
HANDLE hThread, // handle to the thread
LPDWORD lpExitCode // termination status
);
HANDLE CreateThread(
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, // SD /安全属性
DWORD dwStackSize, // initial stack size //线程栈大小-
LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE lpStartAddress, // thread function //线程代码
LPVOID lpParameter, // thread argument //线程参数
DWORD dwCreationFlags, // creation option //创建标识
LPDWORD lpThreadId // thread identifier //线程id
);
创建标志位:
指定一个标志来控制线程的创建,如果指定了 CREATE_SUSPENDED 标志,则线程是在一个挂起状态下创建的,并且在调用了ResumeThread ()函数之前不会运行,如果这个值为零,那么线程在创建之后立即运行
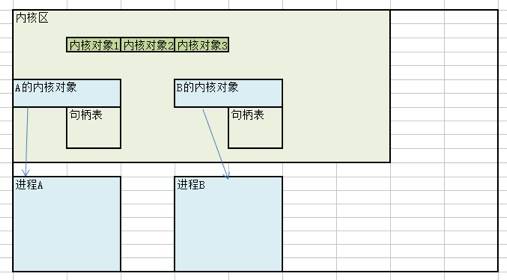
句柄代表着备操作的对象
句柄表可以看做一个非常大的结构体数组
句柄表的结构
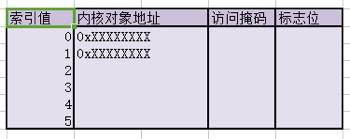
索引值: 进程通过索引找到句柄表中对应的选项
内核对象地址: 通过地址直接找到对应的内核对象
访问掩码: 控制了访问权限
标志位: 标志改句柄能否被继承
//获取控件句柄
HWND GetDlgItem(
HWND hDlg,//获得控件所处的窗口的句柄
int nIDDlgItem //控件id
);
//初始化列表的列 (listview插入新的一列
int ListView_InsertColumn(
HWNDhwnd, //控件的句柄
int iCol, //第几列 (索引 index
const LPLVCOLUMNpcol //结构体指针 (包含新列的结构体
);
//插入新的一行条目
int ListView_InsertItem(
HWND hwnd,
const LPLVITEM pitem
);
//设置条目的属性
BOOL ListView_SetItem(
HWND hwnd,
const LPLVITEM pitem
);
//删除所有项目
BOOL ListView_DeleteAllItems(
HWND hwnd
);
//标准输出格式化字符串
swprintf(buffer,L"%s,哈哈",param);
//清空
ZeroMemory(buffer);
list属性:
//获得进程所使用的堆,模块和线程的信息快照
HANDLE WINAPI CreateToolhelp32Snapshot
(
DWORD dwFlags,//标志位
DWORD th32ProcessID //进程ID
)
//dwFlags: 指定的快照中,指定需要拍的系统部分
TH32CS_INHERIT 声明快照句柄是可继承的。
TH32CS_SNAPALL 在快照中包含系统中所有的 进程和线程。
TH32CS_SNAPHEAPLIST 在快照中包含ID所指定的进程的所有的堆。
TH32CS_SNAPMODULE 在快照中包含在ID所指定的进程的所有的模块。
TH32CS_SNAPPROCESS 在快照中包含系统中所有的进程。
TH32CS_SNAPTHREAD 在快照中包含系统中所有的线程。
BOOL WINAPI Process32First(
HANDLE hSnapshot, //快照句柄
LPPROCESSENTRY32 lppe //获得的信息
);获得快照中的第一个成员的信息
BOOL WINAPI Process32Next(
HANDLE hSnapshot, //快照句柄
LPPROCESSENTRY32 lppe //获得的信息
);获得快照中后一个成员的信息
函数实现
BOOL CreateProcess(
LPCTSTR lpApplicationName, // name of executable module
LPTSTR lpCommandLine, // command line string
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes, // SD
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, // SD
BOOL bInheritHandles, // handle inheritance option
DWORD dwCreationFlags, // creation flags
LPVOID lpEnvironment, // new environment block
LPCTSTR lpCurrentDirectory, // current directory name
LPSTARTUPINFO lpStartupInfo, // startup information
LPPROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation // process information
);
//中文版注释
BOOL CreateProcess(
LPCTSTR lpApplicationName, // 可执行模块名称 (全路径 必须是const字符串
LPTSTR lpCommandLine, // 命令行(字符串 可以不是const字符串
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes, // 进程安全描述符
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, // 线程描述符
BOOL bInheritHandles, // 继承标志位
DWORD dwCreationFlags, // 创建标志位 (指定控制优先级和创建过程的额外标志,除了如前说,可以在任何组合中指定下列创建标标志
LPVOID lpEnvironment, // 进程环境块
LPCTSTR lpCurrentDirectory, // 驱动目录
LPSTARTUPINFO lpStartupInfo, // 启动信息 指向一个窗体结构,该接口体表示新进程的窗口应该如何出现
LPPROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation // 进程信息
);
//启动信息参数的结构体
typedef struct _STARTUPINFO {
DWORD cb; //记录指定结构体大小,以字节为单位
LPTSTR lpReserved;
LPTSTR lpDesktop;
LPTSTR lpTitle; //对于控制台进程,日过创建了新的控制欲窗口,则会显示标题栏中的标题,如果NULL。可执行文件额名称将会用作窗口标题, This parameter must be NULL for GUI or console processes that do not create a new console window.
DWORD dwX; //控制窗口位置x
DWORD dwY; //控制窗口位置y
DWORD dwXSize; //控制窗口宽度
DWORD dwYSize; //控制窗口高度
DWORD dwXCountChars;
DWORD dwYCountChars;
DWORD dwFillAttribute;
DWORD dwFlags;
WORD wShowWindow; //窗口显示方式
WORD cbReserved2;
LPBYTE lpReserved2;
HANDLE hStdInput;
HANDLE hStdOutput;
HANDLE hStdError;
} STARTUPINFO, *LPSTARTUPINFO;
//进程信息结构体
typedef struct _PROCESS_INFORMATION {
HANDLE hProcess; //进程句柄
HANDLE hThread; //主线程句柄
DWORD dwProcessId; //被创建的进程id
DWORD dwThreadId; //被创建的主线程ID
} PROCESS_INFORMATION;
exp: 启动qq
运行中的程序活在内存中 有血有肉有灵魂死在 硬盘上的 有肉没血没灵魂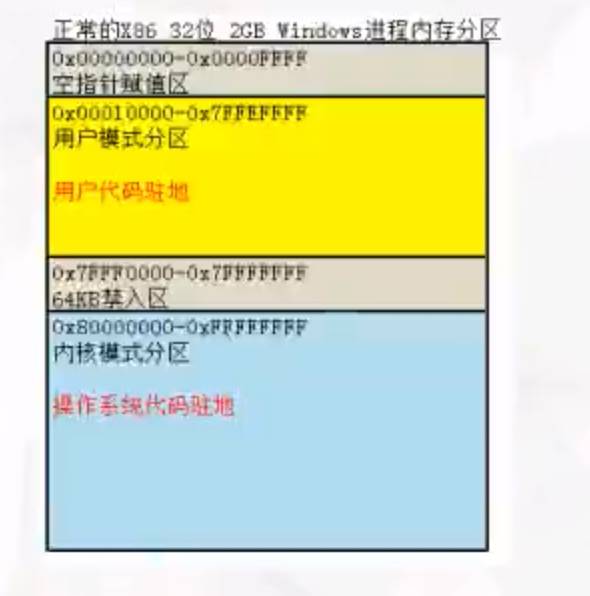
Windows中称为视窗,是一个程序的操作显示界面
Windows中通过什么机制将发生的一些动作和响应的响应函数连接起来
api就是一些预先定义的函数,目的是提供应用程序与开发人员基于某软件或者硬件的一访问一组例程的能力,而又无需访问源码,或者理解内部工作机制的细节
| 数据类型 | 容器、模板 | |
|---|---|---|
| ASCII | 一个字符 | 一个字节 |
| GB码(扩展了的ASCII) | 英文字符 | 一个字节 |
| GB码 | 中文字符 | 两个字节 |
| UNICODE字符集(unicode编码实际指的是utf-16) | 常用字符 | 两个字节 |
宽字符: 用多个字节来表示的字符称之为宽字符(只要不是以单字节存储都可称为宽字符)
由于ASCII存在字符含量过少的缺陷,所以不但我国自己搞出了国际码。其他国家也都设计出了符合自己国情的字符集
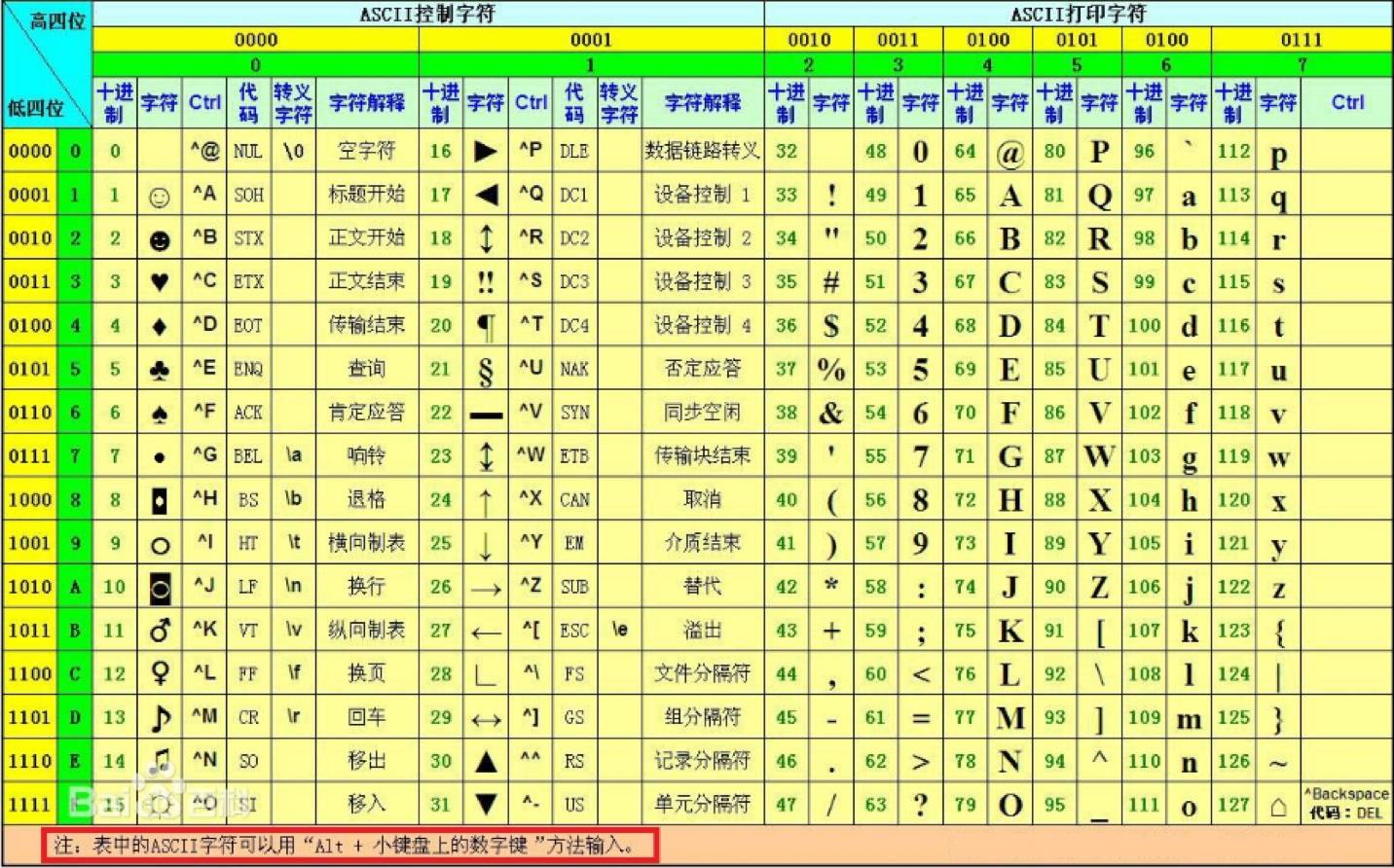
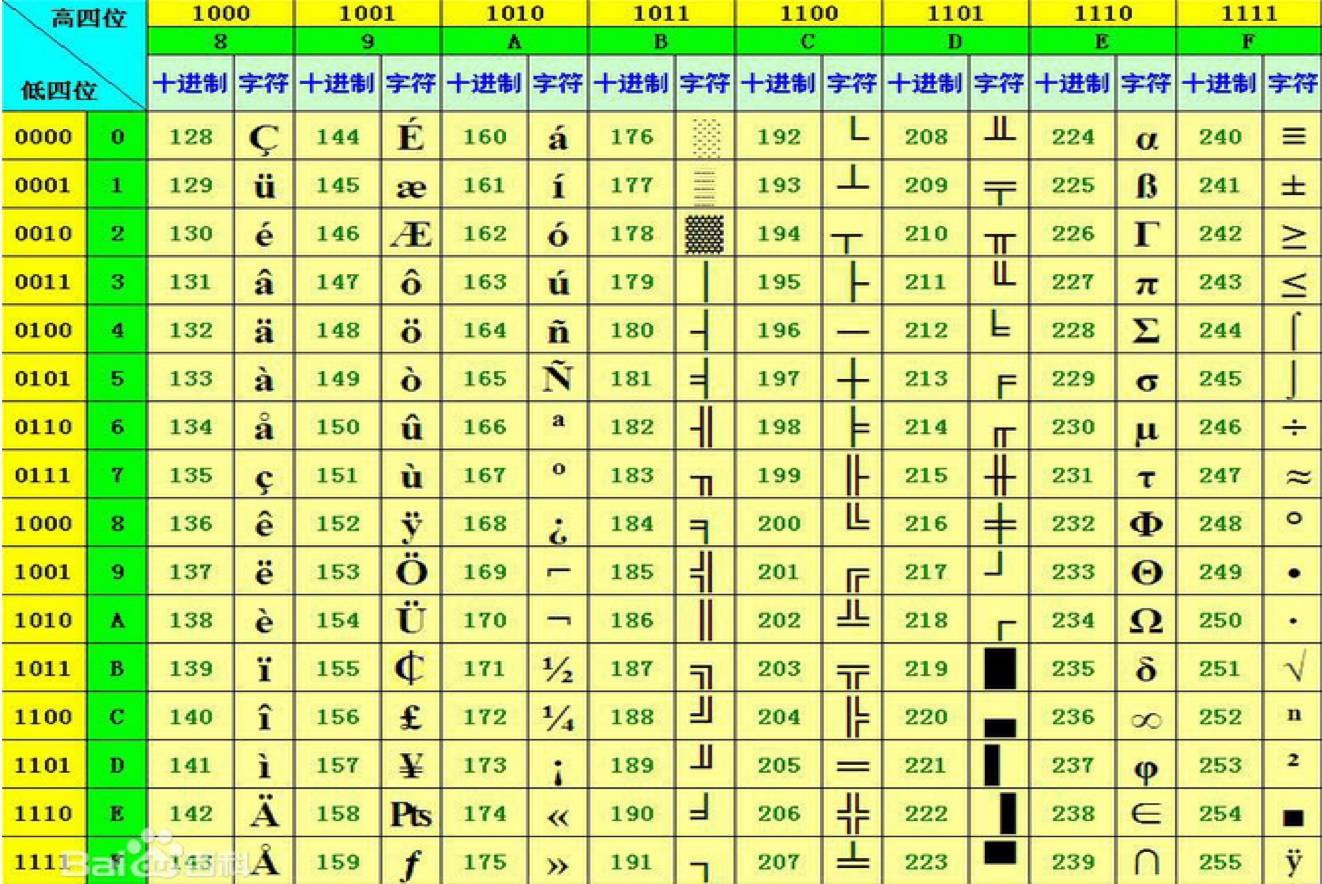
01-09区 为特殊字符区
10-15区 为自定义区
16-87区 为汉字编码区
下面是一个针对int的冒泡排序
// _20180301.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
void Sort(int* arr,int nLength)
{
int i,k;
for (i = 0;ix > base.x && this->y > base.y;
}
private:
int x;
int y;
};
template
void Sort(T* arr,int nLength)
{
int i,k;
for (i = 0;iy)
return x;
else
return y;
}
M min()
{
相同类型间可以直接拷贝
// _20180212.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
class A
{
private:
int* a;
public:
A()
{
a = new int[10];
}
virtual ~A()
{
delete a;
printf("析构 A \n");
}
};
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
A a1;
A a2;
a1 = a2;
return 0;
}
//反汇编
27: A a1;
0040108D lea ecx,[ebp-14h]
00401090 call @ILT+15(B::B) (00401014)
00401095 mov dword ptr [ebp-4],0
28: A a2;
0040109C lea ecx,[ebp-1Ch]
0040109F call @ILT+15(B::B) (00401014)
004010A4 mov byte ptr [ebp-4],1
29: a1 = a2;
004010A8 lea eax,[ebp-1Ch]
004010AB push eax //a2 作为参数传递
004010AC lea ecx,[ebp-14h] //a1 作为this指针传递
004010AF call @ILT+45(A::operator=) (00401032)
30: return 0;
A::operator=:
004012E0 push ebp
004012E1 mov ebp,esp
004012E3 sub esp,44h
004012E6 push ebx
004012E7 push esi
004012E8 push edi
004012E9 push ecx
004012EA lea edi,[ebp-44h]
004012ED mov ecx,11h
004012F2 mov eax,0CCCCCCCCh
004012F7 rep stos dword ptr [edi]
004012F9 pop ecx
//eax = a1首地址
004012FA mov dword ptr [ebp-4],ecx
004012FD mov eax,dword ptr [ebp-4]
//ecx = a2首地址
00401300 mov ecx,dword ptr [ebp+8]
//ecx + 4 这里是 class A中变量a的地址(ecx 对应虚表地址)
//因为ecx是变量a2 所以这里的edx = a2.a
00401303 mov edx,dword ptr [ecx+4]
//a2.a 赋值给a1.a
00401306 mov dword ptr [eax+4],edx
//返回a1首地址
00401309 mov eax,dword ptr [ebp-4]
0040130C pop edi
0040130D pop esi
0040130E pop ebx
0040130F mov esp,ebp
00401311 pop ebp
00401312 ret 4
我们发现使用=直接赋值对象,编译器自动生成了operator= 函数用于处理类型赋值
我们观察编译器自动生成的函数operator=,这里赋值直接略过了虚表(ecx+4)
while
a = 10
while a > 0
puts a
a -= 1
end
until
a = 100
until a == 0
puts a
a -= 1
end
loop
a = 10
loop do
break if a 0
!~ 正则匹配 是否匹配不到 匹配到返回fals 匹配不到返回true
# class_eval
class User
end
User.class_eval do
attr_accessor :name
def hello
"hello"
end
end
user = User.new
user.name = "world"
puts user.name
puts user.hello
# module"s self
module Management
def self.track
"track"
end
end
class User
include Management
end
# User.track # => error
Management.track
# class_eval in project
# requirement: we need to execute a class method when module included
module Manegement
def self.included base #Manafement模块被其他类Included的时候会执行
base.extend ClassMethods #User类注入ClassMethod
base.class_eval do #打开User类
setup_attribute
end
end
# Manegement 内部模块 当引入Management的时候 会被引用为其他类的类方法
module ClassMethods
def setup_attribute
puts "setup_attribute"
end
end
end
class User
include Manegement #目的是在include Management 的时候执行一些方法或者设置
end
# instance_eval, instance methods and class methods
# 1. as a question
class User
end
User.class_eval do
def hello
"hello"
end
end
User.instance_eval do
def hi
"hi"
end
end
puts User.hi
user = User.new
puts user.hello
# puts user.hi #报错
# instance_eval, singleton_method
a = "xxx"
a.instance_eval do
def to_hello
self.replace("hello")
end
end
puts a.to_hello
# b = "world"
# b.to_hello # => error
# class_eval as instance_eval
class User
end
User.class_eval do
def hello
"hello"
end
# works same as instance_eval
def self.hi
"hi"
end
end
puts User.new.hello
puts User.hi
# metho missing
#
# 1. how it works
# 2. ancestors
# 3. rails"s AR
class User
def hello
"hello from User"
end
def method_missing(name, *args)
"method name is #{name} ,parameters :#{args}"
end
end
user = User.new
puts user.hello
puts "-" * 30
puts user.hi("hello",19)
使用::来访问
Array.class # => Class
Class.class # => Class
Array.superclass # =>Object
Object.superclass # =>BasicObject
BasicObject.superclass # => nil
Array.ancestors # => [Array, Enumerable, Object, Kernel, BasicObject]
# class structure, method finding
class User
def panels
@panels ||= ["Profile", "Products"]
end
end
class Admin < User
end
puts Admin.ancestors
admin = Admin.new
p admin.panels
# 从下往上查找 在admin中查找 找不到往上找User 然后Object 然后Kernel 然后 BasicObject
# 重新打开class
class User
def panels
@panels ||= ["Profile", "Products"]
end
end
class User
def panels
"overwrite"
end
end
puts User.ancestors
admin = User.new
p admin.panels
# 从下往上查找 在admin中查找 找不到往上找User 然后Object 然后Kernel 然后 BasicObject
# overwrite and re-open
class Array
def to_hello_word
"hello #{self.join(", ")}"
end
end
a = %w[cat horse dog]
puts a.to_hello_word
# overwrite and re-open
a = %w[cat horse dog]
puts a.join(",")
class Array
def join
"hello"
end
end
puts "-" * 30
puts a.join
Array.ancestors # => [Array, Enumerable, Object, Kernel, BasicObject]
Enumerable.class # => Module
Module.class # => Class
# module acts linke a class
module Management
def company_notifies
"company_notifies from management"
end
end
class User
include Management
def company_notifies
puts super
"company_notifies from user"
end
end
p User.ancestors
puts "-" * 30
user = User.new
puts user.company_notifies
# module included sequence
module Management
def company_notifies
"company_notifies from management"
end
end
module Track
def company_notifies
"company_notifies from track"
end
end
class User
include Management
include Track
def company_notifies
puts super
"company_notifies from user"
end
end
p User.ancestors
puts "-" * 30
user = User.new
puts user.company_notifies
# 1 module included in module
# 2 module acts as class
module Management
def company_notifies
"company_notifies from management"
end
end
module Track
include Management
def company_notifies
puts super
"company_notifies from track"
end
end
p Track.ancestors
puts "-" * 30
include Track
puts company_notifies
# module"s class method
module Management
def self.progress
"progress"
end
# you need to include/extend/prepend to use this metod
def company_notifies
"company_notifies from management"
end
end
puts Management.progress
后面前面# module include
# include
module Management
def company_notifies
"company_notifies from management"
end
end
class User
prepend Management
# include Management
def company_notifies
"company_notifies from user"
end
end
p User.ancestors
puts "-" * 30
user = User.new
puts user.company_notifies
当模块被include时会被执行,同事会传递当前作用于的self对象
# inheritance
class User
attr_accessor :name, :age
def initialize name, age
@name, @age = name, age
end
def panels
# ||= 操作符, 如果变量不存在 那么就赋值
@panels ||= ["Profile", "Products"]
end
end
class Admin < User
def panels
@panels ||= ["Profile", "Products", "Manage Users", "System Setup"]
end
end
user = User.new("user_1", 18)
p user.panels
puts "-" * 30
admin = Admin.new("admin_1", 28)
puts admin.name
p admin.panels
# 查看这个类的父类
p Admin.superclass
super关键字
调用父类的同名方法
self關鍵字
指向當前作用域實例
| |
| |
| |
| |
自己实现 attr_accessor